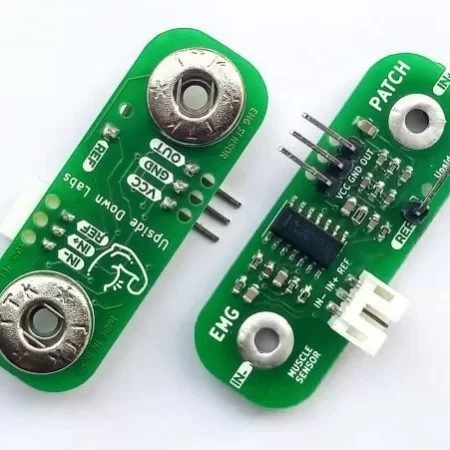
A piezoelectric disc is a type of piezoelectric device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy or vice versa. It is typically made from piezoelectric materials like quartz, ceramic (e.g., PZT – lead zirconate titanate), or other crystals that exhibit the piezoelectric effect.
Key Features of a Piezoelectric Disc:
- Piezoelectric Effect:
- Direct Piezoelectric Effect: When mechanical stress or vibration is applied to the disc, it generates an electrical charge.
- Inverse Piezoelectric Effect: When an electric voltage is applied, the disc deforms or vibrates.
- Applications:
- Sensors: Detecting pressure, force, or vibration (e.g., knock sensors in cars).
- Actuators: Generating precise movements (e.g., in micro-positioning systems).
- Energy Harvesting: Converting ambient vibrations into electrical energy.
- Ultrasonic Devices: Used in medical imaging, cleaning, or distance measurement.
- Buzzers and Speakers: Generating sound by vibrating at specific frequencies.
- Advantages:
- High sensitivity to mechanical stress.
- Fast response time.
- Compact and lightweight.
- Can operate over a wide frequency range.
- Limitations:
- Fragile and can break under excessive stress.
- Limited power output for energy harvesting applications.
- Sensitive to temperature changes.
How It Works:
- When the disc is mechanically deformed, the internal dipoles in the material align, creating a voltage across the electrodes.
- Conversely, applying a voltage causes the material to expand or contract, producing mechanical motion.
Common Specifications:
- Diameter: 27mm
- Thickness: 1mm










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.